EKF SLAM from scratch
ProjectThis project implements an Extended Kalman Filter(EKF) Simultaneous Localization and Mapping(SLAM) algorithm from scratch using ROS2 on a turtlebot 3 coded in C++. The robot is equipped with a LIDAR sensor that provides range and bearing measurements to landmarks in the environment. The EKF SLAM algorithm estimates the robot’s position and the position of the landmarks in the environment using these sensor measurements.
Video Demo
- Red represents the ground truth of the robot position and path, landmark and wall positions
- Blue represents the odometry estimate of the robot position and path
- Green represents the estimated position of the robot and the landmarks using the EKF SLAM algorithm.
- Yellow obstacles represent the simulated sensor data
Library and Packages
- turtlelib: custom library built to manage the 2D geometry math, the differential drive of the turtlebot, and the landmark detection.
- nusim: the package that handles the simulation and representation of the turtlebots in rviz
- nuturtle_description: the meshes and urdf of the turtlebot
- nuturtle_control: the package that controls the movement of the turtlebots and the conversion of messages and services
- nuslam: the package that handles the ekf-slam algorithm to localize the turtlebot
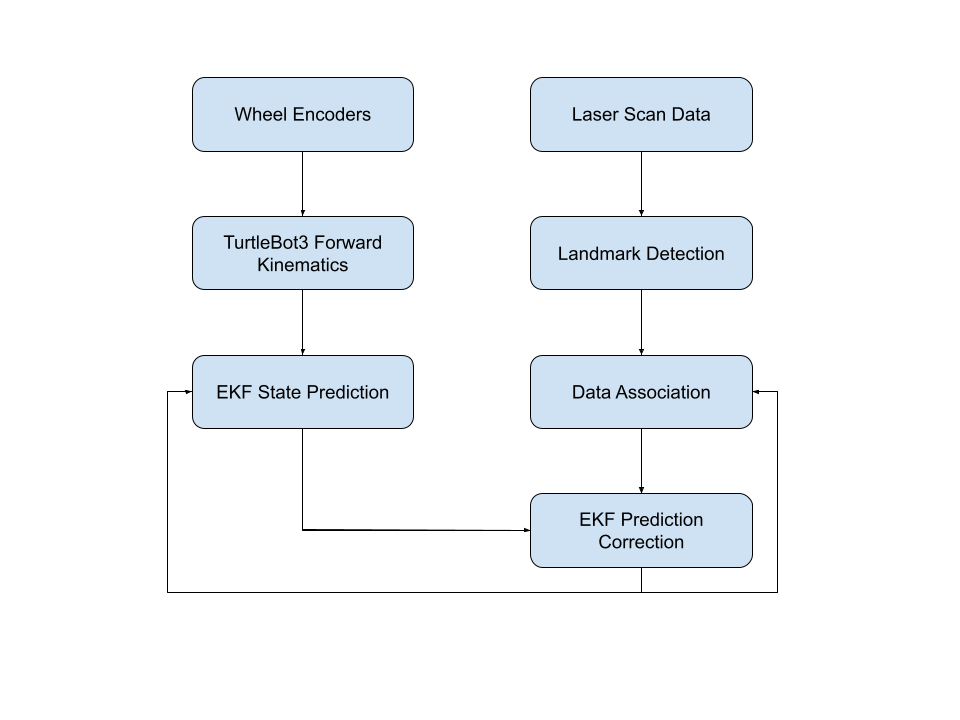
Algorithm Description
Feature-based Extended Kalman Filter SLAM is performed to provide accurate odometry position of the turtlebot using two sources of data: Odometry calculations and Fake Sensor Data. The odometry data is calculated with sensor noise and the Fake Sensor Data represents the data that the LiDAR would output after going through Landmark Detection and Data Association algorithms.
EKF SLAM is performed in two main steps: Prediction and Correction. Below is a pipeline of the algorithm.